Why is Vitamin E an underestimated nutrient? In addition to evidence showing that Vitamin E plays a role in vision, reproductive, cardiovascular and brain health, Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that limits the body’s inflammatory response. It’s one reason why studies have focused on the role of Vitamin E, particularly in adults with chronic inflammation.
There’s evidence suggesting increased Vitamin E intake can improve immune function and inflammatory processes, helping the body resist infection. It accomplishes this in part by combatting oxidative stress that can cause damage to cells—and even cell death.
While research is ongoing, studies support the belief that Vitamin E can act as a potent defense against oxidative stress and the development of serious degenerative diseases.
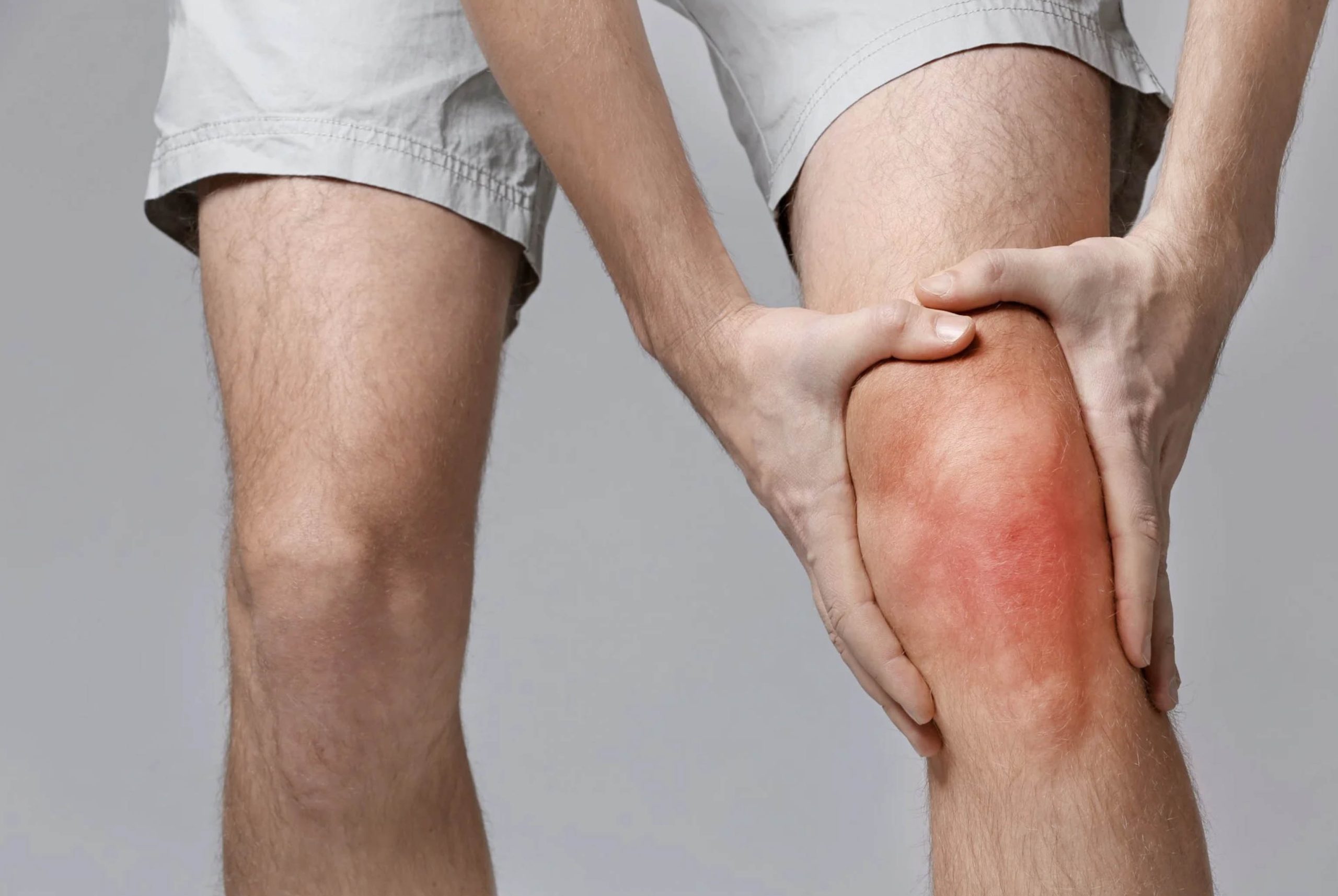
Inflammation is a leading cause of death
There are several social, environmental and lifestyle factors that contribute to inflammation. Left unchecked over time, a person can develop systemic chronic inflammation (SCI), a marker for several diseases, including cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, liver disease and autoimmune and neurodegenerative disorder. Together, these diseases represent the leading causes of disability and death worldwide.
Scientists recognize that chronic inflammatory diseases are the most significant cause of death throughout the world. It follows that limiting the body’s inflammatory response can be a way to fight serious, fatal diseases.
The anti-inflammatory benefits of tocopherol
The tocopherols are a group of Vitamin E isomers that neutralize free radicals that contribute to the development of inflammation. They’re stored in the body’s fat cells and are released when the body detects the presence of an imbalance of free radicals. As they work to counteract free radicals, tocopherols prevent oxidative stress from harming cells and triggering the body’s immune response and, by consequence, inflammation.
Alpha-tocopherol is the most significant isomer in the tocopherol group. It represents the isomer with the highest Vitamin E bioavailability and utility in humans, effectively counteracting free radical damage. Studies have shown that alpha-tocopherol is a powerful anti-inflammatory. In particular, alpha-tocopherol therapy at high doses has been shown to decrease the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Research is ongoing, but early studies have been promising in terms of alpha-tocopherol’s beneficial role in fighting inflammation.
Vitamin E could hold the secrets to inflammation control
Scientists studying chronic inflammation have found that Vitamin E can be effective in reducing the body’s inflammatory response. There is a growing consensus that Vitamin E can be beneficial for individuals with chronic inflammation, especially elderly patients or those with type II diabetes or heart failure.
Since Vitamin E supplements are already approved and safe for consumption under a doctor’s supervision, reducing chronic inflammation can be an additional benefit to boosting the body’s Vitamin E levels.
Studies about inflammation are ongoing
Chronic inflammation is linked to a range of serious diseases, many of which are life-threatening. There are a variety of effective strategies that can ward off inflammation, including medication, stress-reduction, exercise and following a diet rich in anti-inflammatory whole foods. Many people also turn to supplements, in particular Vitamin E in its alpha-tocopherol form.
While research continues regarding the role of Vitamin E in combatting inflammation, including systemic chronic inflammation, results have been promising. If you’re considering complementing a healthy lifestyle with a Vitamin E supplement, reach out to your doctor for professional guidance. Don’t hesitate to talk to your doctor and see whether Vitamin E can be an effective defense against the threat of inflammation.
Products you might be interested in: